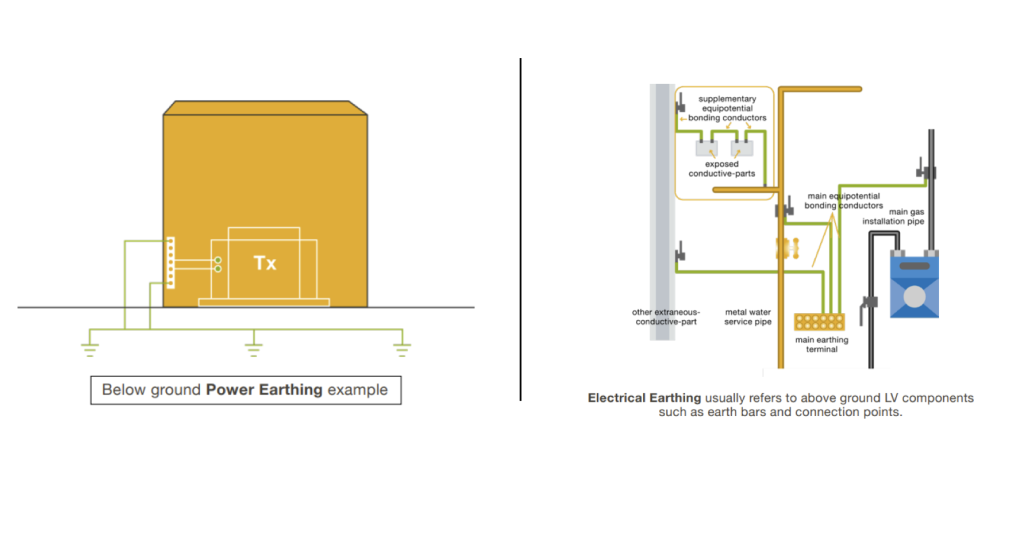
What’s the difference?
Electrical Earthing and Power Earthing systems also known as grounding, are both processes that connect an electrical system to the ground for safety and functionality.
The main difference between the two is that Electrical Earthing usually relates to anything above ground such as circuit protective conductors and equipotential bonding.
Power Earthing (also known as grounding or earthing) relates to the process of connecting electrical systems to a grounding system or electrodes buried in the ground.
Power Earthing Systems should be inspected and tested at regular intervals to remain compliant
-
Employers & Business owners have a legal responsibility under The Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 to protect employees from threats arising from faulty electrical wiring and installations.
-
As the last line of defence against dangerous electrical faults occurring, Power Earthing Systems must be inspected and tested at regular intervals to ensure they remain effective.
-
BS 7430:2015 Code of Practice for Protective Earthing of Electrical Installations.
-
BS EN 50522: 2022 Earthing of Power Installations Exceeding 1kV AC.
-
ENA Technical Specification 41-24 Guidelines for the design, installation, testing andmaintenance of main earthing systems in substationsPower Earthing Inspections are required in accordance with:
-
HTM 06-03 Appx 1 Protective, test and earthing equipment (page 69)
-
HTM 06-01 Electrical services supply and distribution Chapter 13 Earthing
-
WHTM 06-03 A1 Protective, test and earthing equipment part 42 Substation Earthing(page 97)
-
WHTM 06-01 Electrical services supply and distribution Chapter 13 Earthing
-
WHTM 06-02 A1 Protective, test and earthing equipment Appendix 1 Protective, test andearthing equipment
-
SFG20 Building Maintenance Standard, HOSPITALS AND HEALTHCARE PREMISES – Health Technical Memorandum requirementsInspection Schedule:
-
Visual inspection annually
-
Full test and maintenance of system to be carried out at a period not exceeding 5 years
-
Only trained and competent power earthing engineers should perform these testsPower Earthing systems play a critical role in maintaining site safety—protecting personnel, equipment, and your entire facility from unexpected electrical faults.
A TYPICAL TEST INCLUDES THE FOLLOWING
Survey and record the location of existing, earth bars, earth bar bonding conductors, and earth electrodes on site associated with Power Earthing Systems.
Undertake “fall of Potential” earth resistance testing of existing earth electrodes. The measurement instrument should inject a square wave DC current at 128Hz.
Within each substation’s local environment, undertake continuity measurements from the main earth bar to all equipment within said substation.
Record all power earthing system conductor CSA sizes
Continuity measurements should be undertaken utilising a low resistance (micro) /high current Ohmmeter.
Undertake Earth Resistance Clamp Meter Testing where it is impractical to carry out a Fall of Potential test.
Measurements should be undertaken utilising a DET 14/C Earth Clamp-on Tester.
Assess the adequacy of existing earthing infrastructure and provide all findings and test results in a concise formal report.
Where the existing earthing system response to fault conditions proves inadequate under the study; provide recommendations on any remedial/ improvement works required to meet with current national standards:
A failed earthing system can have serious consequences, including:
-
Electric shock: People can be electrocuted if the power earthing system is ill maintained or insufficient (not fit for the purpose intended).
-
Fires: Sparks and arcs caused by an earth fault can lead to fires.
-
Equipment damage: Without adequate grounding, equipment can experiencevoltage surges and spikes that can cause catastrophic damage.
-
Loss of data: A failed earthing system can lead to the loss of mission-critical data.
-
Increased costs: Equipment may need to be replaced due to damage.
-
Safety risks: Faults that aren’t isolated quickly can create dangerous conditions for people and infrastructure.The Key Benefits of Power Earthing Testing:
-
Enhanced Safety: Prevent potential hazards caused by electrical faults with reliablepower earthing systems.
-
Operational Reliability: Reduce unexpected downtimes and protect sensitive equipment.
-
Compliance Assurance: Meet industry and regulatory standards with certified testing.
-
Proactive Maintenance: Identify and resolve issues before they become dangerous andpotentially fatal.
-
Our team of qualified and experienced professionals uses advanced diagnostic tools to provide detailed assessments and recommendations, ensuring your power earthing system operates optimally
-
Power Earthing @ PTSG offers a comprehensive range of power earthing solutions, including survey, test & inspection, design and installation
-
For complete peace of mind, don’t leave your safety to chance
To schedule your power earthing inspection or to discuss any other power earthing requirements please contact the Power Earthing team @ PTSG: Email: [email protected] Telephone: 0115 9758 835